Synchronized Swimming: Artistry Meets Athleticism
Synchronized swimming, a captivating blend of dance, gymnastics, and swimming, has long been a source of fascination for spectators and athletes alike. This aquatic sport demands an extraordinary combination of strength, flexibility, and artistic expression, all while performers execute intricate routines submerged in water. As we dive into the depths of this unique discipline, we'll explore its rich history, technical challenges, and the evolving landscape of competitive synchronized swimming on the global stage.
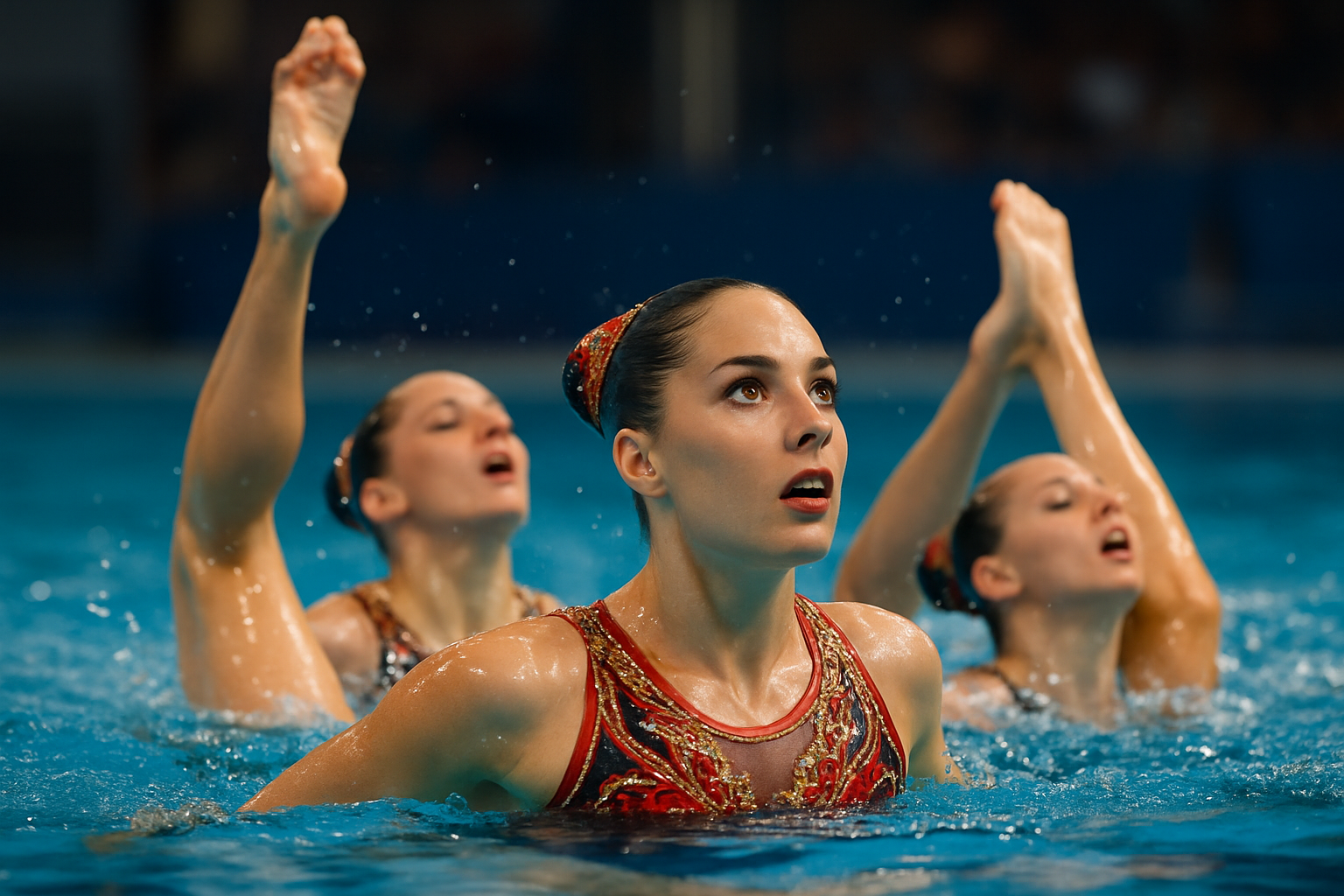
The Birth of a Water Ballet
Synchronized swimming’s roots can be traced back to the late 19th and early 20th centuries, when “water ballets” began to gain popularity in Europe and North America. These performances, often featuring elaborately costumed swimmers executing choreographed routines, were primarily entertainments at hotels and aquatic shows. The sport’s competitive aspect began to take shape in the 1930s, largely due to the efforts of Katherine Curtis, an American swimming instructor who organized the first synchronized swimming competition in Chicago in 1939.
Curtis’s work laid the foundation for the sport’s development, but it was the involvement of Hollywood that truly catapulted synchronized swimming into the public eye. Esther Williams, a competitive swimmer turned actress, starred in a series of aquatic-themed musical films in the 1940s and 1950s. These “aquamusicals” featured elaborate synchronized swimming routines that captured the imagination of audiences worldwide and helped popularize the sport.
As interest grew, so did the need for standardization and organization. In 1952, the Fédération Internationale de Natation (FINA) recognized synchronized swimming as an official discipline, paving the way for its inclusion in international competitions. The sport made its Olympic debut as a demonstration event at the 1984 Los Angeles Games and became a full medal event at the 1984 Olympics in Seoul.
The Technical Marvels of Synchronized Swimming
At first glance, synchronized swimming might appear to be all about graceful movements and stunning formations. However, beneath the surface lies a world of intense physical demands and technical precision. Synchronized swimmers are often considered some of the most well-rounded athletes in the world, combining the endurance of long-distance swimmers, the strength of water polo players, and the flexibility of gymnasts.
One of the most challenging aspects of the sport is the requirement for athletes to perform complex routines while holding their breath for extended periods. Synchronized swimmers often spend up to a minute underwater during a routine, executing intricate movements with their legs while keeping their upper bodies still and smiling above the surface. This demands not only exceptional lung capacity but also precise breath control and the ability to maintain composure under extreme physical stress.
The “eggbeater” kick, a fundamental technique in synchronized swimming, is a prime example of the sport’s technical complexity. This treading water technique allows swimmers to maintain a stable vertical position while keeping their upper body above the water, often with their arms raised. Mastering the eggbeater kick requires years of practice and incredible leg strength, as swimmers must generate constant upward force to counteract their body weight.
Choreography and Artistic Expression
While the physical demands of synchronized swimming are undeniable, the sport’s artistic elements are equally crucial. Routines are carefully choreographed to music, with movements designed to tell a story or evoke specific emotions. Swimmers must not only execute complex techniques flawlessly but also interpret the music and convey artistic expression through their performance.
The choice of music and theme for a routine is a critical decision that can significantly impact a team’s success. Coaches and choreographers work together to select music that complements the swimmers’ strengths and allows for creative interpretation. Themes can range from classical ballet to contemporary dance, often incorporating cultural elements or storytelling aspects.
Costume design is another essential component of artistic expression in synchronized swimming. Suits are typically adorned with sequins and other embellishments to catch the light and enhance the visual impact of the performance. However, these costumes must also be functional, allowing for ease of movement in the water and remaining secure during complex maneuvers.
Training Regimens: The Path to Perfection
The journey to becoming an elite synchronized swimmer is one of dedication, discipline, and relentless practice. Training routines for competitive synchronized swimmers are among the most demanding in any sport, often involving up to eight hours of daily practice, six days a week.
A typical training day might begin with land exercises focused on flexibility, strength, and endurance. Yoga and Pilates are commonly incorporated to improve core strength and body control. Gymnastic training is also frequently included to enhance acrobatic skills and body awareness.
In-pool training sessions focus on perfecting technical skills, such as figures and lifts, as well as rehearsing routines. Swimmers spend countless hours working on synchronization, timing, and spatial awareness. Underwater speakers allow teams to practice their routines to music, ensuring perfect timing and coordination.
One of the most challenging aspects of training is developing the ability to hold one’s breath for extended periods. Synchronized swimmers use various techniques to increase their lung capacity and breath control, including hypoxic training and specialized breathing exercises. Some elite swimmers can hold their breath for up to four minutes, a skill that requires years of dedicated practice to achieve.
The Global Stage: Competitions and Championships
Synchronized swimming competitions are held at various levels, from local club meets to international championships and the Olympic Games. At the highest level, the sport is divided into several events: solo, duet, team, and combination. Each event has its own set of rules and judging criteria, but all share a focus on technical merit and artistic impression.
The World Aquatics Championships, held biennially, is one of the most prestigious events in the synchronized swimming calendar. This competition brings together the world’s best swimmers to compete in various aquatic disciplines, including synchronized swimming. The event serves as a showcase for new techniques and choreography, often setting trends that influence the sport’s development.
At the Olympic level, synchronized swimming currently features two events: duets and teams. The competition is fierce, with nations like Russia, China, and Spain traditionally dominating the medal standings. However, the landscape is constantly evolving, with countries like Japan, Ukraine, and Canada making significant strides in recent years.
Judging and Scoring: The Art of Evaluation
Evaluating synchronized swimming performances is a complex process that requires a keen eye for both technical execution and artistic merit. Judges assess routines based on a variety of criteria, including:
-
Technical Merit: This includes the execution of figures, transitions, and patterns, as well as the difficulty of the routine.
-
Artistic Impression: Judges evaluate the choreography, interpretation of music, and overall presentation.
-
Synchronization: The precision with which swimmers move in unison is a crucial factor in scoring.
-
Use of the Pool: Effective use of space and the creative incorporation of different areas of the pool are considered.
-
Difficulty: More challenging elements and combinations receive higher scores.
Scoring in synchronized swimming has evolved over the years to become more objective and transparent. The current system uses a combination of technical and artistic scores, with deductions for errors or lack of synchronization. Despite these efforts, judging in synchronized swimming remains somewhat subjective, and controversies over scoring are not uncommon in high-level competitions.
The Evolution of Mixed Duets
One of the most significant developments in recent years has been the introduction of mixed duets in international competition. Traditionally a female-dominated sport, synchronized swimming has begun to embrace gender inclusivity with the addition of male swimmers in duet events.
The first World Championships to feature mixed duets was in Kazan, Russia, in 2015. This groundbreaking event marked a new chapter in the sport’s history, challenging traditional gender roles and opening up new possibilities for artistic expression and technical innovation.
Mixed duets have brought fresh energy and diversity to synchronized swimming, allowing for new types of lifts and formations that take advantage of the different strengths of male and female swimmers. While still a relatively new addition to the competitive landscape, mixed duets have already gained a significant following and are pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in the sport.
Technological Advancements in Training and Performance
As with many sports, technology is playing an increasingly important role in synchronized swimming. From underwater cameras that allow coaches to analyze swimmers’ movements in real-time to advanced software for choreography planning, technology is helping athletes and coaches push the limits of performance.
One area where technology has made a significant impact is in music editing and underwater sound systems. High-quality underwater speakers ensure that swimmers can hear their music clearly throughout their routine, even when fully submerged. Advanced music editing software allows coaches to create precise cuts and mixes that perfectly match the desired choreography.
Wearable technology is also finding its place in synchronized swimming training. Devices that measure heart rate, oxygen levels, and other physiological markers can help coaches optimize training regimens and monitor athletes’ health and performance. Some teams are even experimenting with virtual reality systems to help swimmers visualize and practice routines out of the water.
Challenges and Controversies
Despite its beauty and athleticism, synchronized swimming faces several challenges as it seeks to maintain and grow its place in the world of competitive sports. One ongoing issue is the perception of the sport as being less physically demanding than other aquatic disciplines. This misconception can impact funding, media coverage, and athlete recruitment.
Another challenge lies in the judging system. While efforts have been made to make scoring more objective, the inherent artistic element of the sport means that some degree of subjectivity is unavoidable. This can lead to controversies and debates over scoring decisions, particularly in high-stakes competitions.
The sport has also faced criticism for its emphasis on a particular body type and appearance. Traditionally, synchronized swimmers have been expected to maintain a lean, athletic physique, and there have been concerns about unhealthy body image pressures within the sport. In recent years, there has been a push for greater body diversity and a focus on overall health and performance rather than appearance.
The Future of Synchronized Swimming
As synchronized swimming continues to evolve, several trends are shaping its future:
-
Increased Athleticism: Routines are becoming increasingly acrobatic, with more complex lifts and throws being incorporated.
-
Technological Integration: From training aids to performance analysis, technology is likely to play an even larger role in the sport’s development.
-
Gender Inclusivity: The success of mixed duets may lead to further integration of male swimmers in other events.
-
Global Expansion: While traditionally dominated by a few countries, the sport is gaining popularity in new regions, potentially changing the competitive landscape.
-
Artistic Innovation: As the sport matures, we can expect to see more diverse and experimental choreography and musical choices.
Synchronized Swimming Beyond Competition
While competitive synchronized swimming garners the most attention, the sport has applications beyond the world of elite athletics. Many synchronized swimming clubs offer programs for recreational swimmers of all ages, providing a unique form of exercise that combines cardiovascular fitness, strength training, and artistic expression.
Synchronized swimming has also found a place in therapy and rehabilitation. The low-impact nature of water-based exercise, combined with the focus on controlled movements and breath control, makes it an excellent option for individuals recovering from injuries or managing chronic conditions.
In the entertainment world, synchronized swimming continues to captivate audiences. Water shows featuring synchronized swimming routines are popular attractions at resorts and theme parks around the world. These performances often incorporate elements of circus arts and theatrical production, pushing the boundaries of what’s possible in aquatic entertainment.
The Impact of Synchronized Swimming on Athletes
For those who dedicate themselves to synchronized swimming, the sport offers benefits that extend far beyond the pool. The discipline required to excel in this demanding sport often translates to success in other areas of life. Many synchronized swimmers report that their training has helped them develop strong time management skills, resilience in the face of challenges, and the ability to work effectively as part of a team.
The unique combination of athletic and artistic elements in synchronized swimming also fosters creativity and self-expression. Athletes often speak of the sense of freedom and joy they experience when performing, despite the physical demands of the sport. This blend of physicality and artistry can have a profound impact on an athlete’s personal development and self-confidence.
Moreover, the sport’s emphasis on teamwork and precise coordination helps develop strong interpersonal skills. Synchronized swimmers must learn to communicate effectively, both verbally and non-verbally, and to trust their teammates implicitly. These skills often prove valuable in various professional and personal contexts long after an athlete’s competitive career has ended.
Synchronized Swimming and Cultural Exchange
As an international sport, synchronized swimming serves as a platform for cultural exchange and understanding. Teams from different countries often incorporate elements of their national culture into their routines, showcasing traditional music, dance styles, or themes that reflect their heritage.
International competitions provide opportunities for athletes from diverse backgrounds to come together, share experiences, and learn from one another. This cultural exchange extends beyond the pool, as teams often participate in cultural activities and form lasting friendships with competitors from other nations.
The sport’s global nature also contributes to its evolution, as techniques and styles from different regions influence and inspire one another. This cross-pollination of ideas helps drive innovation in choreography, training methods, and performance techniques, ensuring that synchronized swimming continues to grow and adapt.
Environmental Considerations in Synchronized Swimming
As awareness of environmental issues grows, the world of synchronized swimming is also grappling with questions of sustainability and ecological impact. The maintenance of large pools requires significant energy and water resources, leading some organizations to explore more sustainable practices.
Some facilities are implementing energy-efficient heating and filtration systems, while others are exploring the use of natural or recycled water sources. There’s also growing attention to the environmental impact of swimwear and costume materials, with some teams and manufacturers looking into more eco-friendly options.
Additionally, as climate change affects water resources in many parts of the world, the sport may need to adapt. Some regions are exploring the potential for synchronized swimming in natural bodies of water, which could present new challenges and opportunities for the sport.
The Role of Media and Social Platforms
In the digital age, synchronized swimming is finding new ways to connect with audiences and attract new participants. Social media platforms have become powerful tools for athletes and teams to share behind-the-scenes glimpses of their training, showcase their artistry, and engage with fans.
Video-sharing platforms have been particularly instrumental in raising the sport’s profile. Slow-motion and underwater footage of synchronized swimming routines often go viral, showcasing the incredible athleticism and grace of the performers to a wide audience.
These platforms also serve as valuable resources for aspiring synchronized swimmers, providing access to training tips, technique demonstrations, and inspiration from elite athletes. This democratization of information is helping to grow the sport at the grassroots level, potentially broadening the talent pool for future competitive swimmers.
Conclusion: The Enduring Allure of Synchronized Swimming
Synchronized swimming stands as a testament to the incredible capabilities of the human body and spirit. It is a sport that demands not only peak physical condition but also artistic sensitivity, mental fortitude, and unwavering teamwork. As it continues to evolve, synchronized swimming pushes the boundaries of what’s possible in the water, challenging athletes to reach new heights of performance and creativity.
From its origins as a form of aquatic entertainment to its current status as a highly competitive Olympic sport, synchronized swimming has captivated audiences and inspired athletes for generations. Its unique blend of athleticism and artistry offers a spectacle unlike any other in the world of sports, inviting viewers to marvel at the grace and power on display.
As we look to the future, synchronized swimming seems poised to continue its growth and evolution. With ongoing innovations in training techniques, technology integration, and artistic expression, the sport is likely to reach new levels of complexity and beauty. At the same time, efforts to increase inclusivity and address environmental concerns promise to make synchronized swimming more accessible and sustainable.
Whether viewed as a competitive pursuit, a form of artistic expression, or a unique way to stay fit, synchronized swimming offers something truly special. It reminds us of the magic that can happen when human skill and creativity meet the transformative power of water, creating a symphony of movement that continues to inspire and amaze.




